Application Report
SLUA312 − May 2004
1
200-W Interleaved Forward Converter Design Review
Using TI’s UCC28221 PWM Controller
Michael O’Loughlin System Pow
er
ABSTRACT
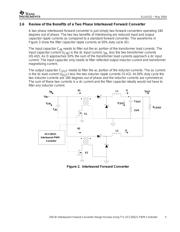
Interleaved buck converters are widely used in the personal computer industry in voltage
regulation module (VRM) applications to power central processing units, CPUs, like the
Pentium 4 and Athlon. This topology is widely used due to the reduced input and output
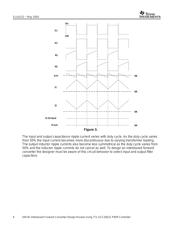
capacitor ripple current that is gained by interleaving the converters as compared to a single
buck power stage. The reduction in input and output capacitor RMS currents allows the
designer to reduce the input and output capacitor banks that are required for the design. The
same benefits that are gained from interleaving buck converters can be gained from
interleaving forward converters. In high current applications such as telecom dc-to-dc
converters reducing the input and output capacitor banks can reduce the size and cost of the
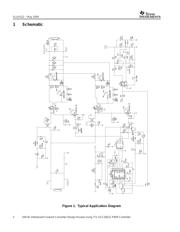
design. This application note reviews the design of a telecom converter that converts a
telecom input range of 36 V to 75 V dc down to a regulated 12-V, 200-W dc output. The design
information in this application note is used in the design of the UCC28221 Evaluation Module
(EVM) HPA035 [5].
Table 1. Applicable Devices
MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Input voltage (V
IN
) 36 75 V
Output voltage (V
OUT
) 11.4 12 12.6 V
Output power (P
OUT
) 50 200 W
Switching frequency (f
S
) 500 kHz
Efficiency at maximum output power (η) 85%
Maximum duty cycle (D
MAX
) 50%
Input voltage ripple (V
IN(ripple)
) 1 V
Output voltage ripple (V
OUT(ripple)
) 200 mV
NOTES:This design was based on typical design values.