下载

Technical Brief
SWRA030
Digital Signal Processing Solutions May 1999
Understanding and Enhancing Sensitivity in
Receivers for Wireless Applications
Edited by Matt Loy Wireless Communication Business Unit
Abstract
This technical brief provides an overview of communication receiver sensitivity. One of the most
important parameters in determining the overall performance of a communication system,
receiver sensitivity translates directly into communication distance and reliability.
A few receiver architectures can offer dependable communication at low cost, if proper design
procedures and trade-offs are implemented. RF amplifiers, mixers, and filters are common circuit
building blocks for every architecture. System performance is tied to each individual block
comprising the receiver. Each circuit generates noise that degrades reception of the desired
signal.
Understanding noise sources and the methods of minimizing degradation allows optimal design
trade-offs for a given cost. Circuit nonlinearity causes undesired signals to hinder the reception of
desired signals. A low-noise system design typically does not produce the best linearity, and high
linearity typically produces more noise. A thorough understanding of the receiver RF environment
can help your design achieve the proper specifications for optimal noise and linearity.
Contents
Introduction...............................................................................................................................................4
Receiver Architectures..............................................................................................................................4
Homodyne (Zero IF) Receiver.........................................................................................................4
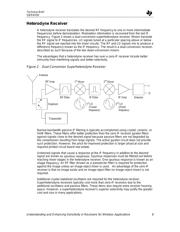
Heterodyne Receiver......................................................................................................................6
Access Methods and Modulation Schemes................................................................................................7
Access Methods.............................................................................................................................7
Modulation Schemes....................................................................................................................10
Receiver Building Blocks......................................................................................................................... 16
Antenna....................................................................................................................................... 17
Duplexers ....................................................................................................................................18
Low-Noise Amplifier (LNA) ........................................................................................................... 19
RF Filters..................................................................................................................................... 19
Mixers.......................................................................................................................................... 20
Local Oscillator ............................................................................................................................ 22
IF Filter........................................................................................................................................ 23
IF Amplifier ..................................................................................................................................23
Detectors.....................................................................................................................................24
Receiver Sensitivity.................................................................................................................................24
Noise of Two-Port Networks......................................................................................................... 25
Noise Temperature....................................................................................................................... 29