下载

Application Report
SPRAB25 – January 2009
How to Approach Inter-Core Communication on
TMS320C6474
Juergen Mathes ...............................................................................................................................
ABSTRACT
Today’s digital signal processor (DSP) architectures are confronted with the tough
requirement of addressing a wide-range of standards and meeting a cost-effective
performance/power trade-off. Increasing raw million instructions per second (MIPS)
performance just by running at a higher frequency is not possible anymore since
leakage is becoming a dominant factor with shrinking silicon geometries. One vector in
scaling modern processing architectures is the number of cores on a single piece of
silicon. It becomes crucial to find the sweet spot of performance and power
consumption.
Having said this, the question is how to ease the handling of the three cores that are
present on the C6474? What features are supported and how can they be used? How
do the cores communicate effectively with each other on the chip? How is scalability
allowed on board level? This application report offers some answers to those
questions.
Contents
1 Why Move Towards Multi-Core? ................................................................. 2
2 C6474 Architecture Overview ..................................................................... 2
3 Features That Support a Multi-Core Architecture on the C6474 ............................. 4
4 Software Support ................................................................................... 8
5 On-Board vs On-Chip Communication .......................................................... 9
6 References .......................................................................................... 9
Appendix A Example Scenarios ..................................................................... 10
List of Figures
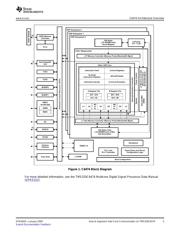
1 C6474 Block Diagram .............................................................................. 3
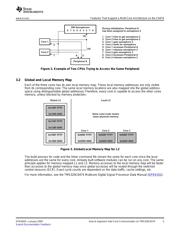
2 Example of Two CPUs Trying to Access the Same Peripheral .............................. 5
3 Global/Local Memory Map for L2 ................................................................. 5
4 Example of Access Violation ...................................................................... 6
5 Event Architecture .................................................................................. 8
A-1 Proxied Memory Protection ...................................................................... 13
List of Tables
A-1 Comparison of Data Copy/Move vs Sharing .................................................. 11
C64x+, DSP/BIOS, TMS320C5000, TMS320C6000, Code Composer Studio, C6000 are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
RapidIO is a registered trademark of RapidIO Trade Association.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
SPRAB25 – January 2009 How to Approach Inter-Core Communication on TMS320C6474 1
Submit Documentation Feedback