下载
Application Report
SLLA106 - February 2002
1
TIA/EIA-485 and M-LVDS, Power and Speed Comparison
Chris Sterzik Interface Products
ABSTRACT
This document includes 3.3 V RS-485 and 3.3 V M-LVDS test data to demonstrate that
M-LVDS provides low power multipoint operation and faster signaling rates (speeds) than
RS-485.
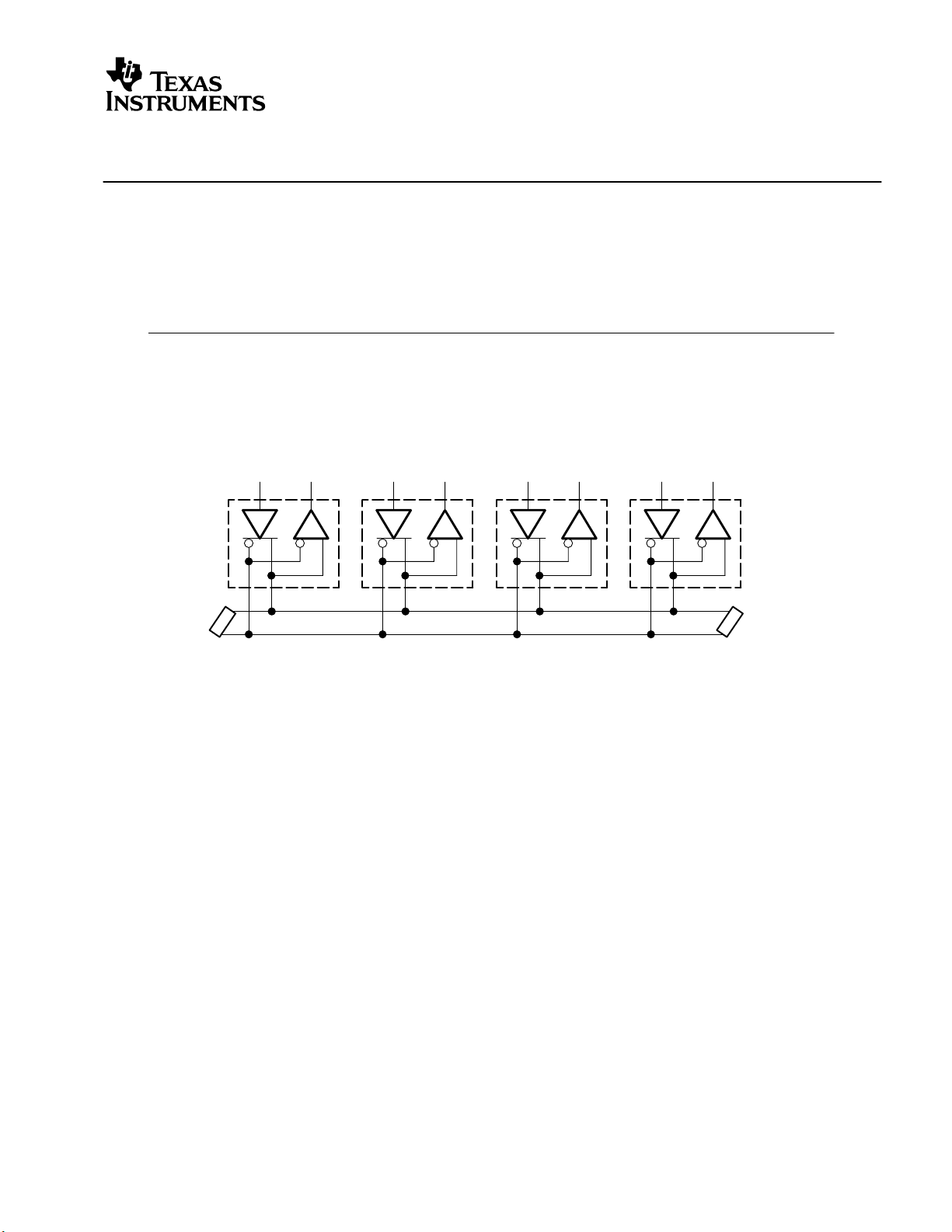
Multipoint is a bus configuration with multiple drivers and receivers present, as shown in
Figure 1. An example of a differential multipoint standard is TIA/EIA-485 (RS-485). RS-485 is an
established standard and is used in industrial, automotive, telecom, computer, and many other
applications. The benefits of RS-485 include high-common mode range, high differential output
signal, and the capability to drive beyond 1 km. All of these benefits lend RS-485 to applications
where noise margin and distance are significant factors.
Figure 1. Multipoint Architecture
Another example of differential multipoint operation is the new M-LVDS standard, TIA/EIA-899
Electrical Characteristics of Multipoint-LVDS (M-LVDS) Interface Circuits for Multipoint Data
Interchange. The M-LVDS standard is an extension of LVDS technology into the multipoint
environment, providing support for speeds (signaling rates) up to 500Mbps. Devices compliant
with the M-LVDS standard do not provide as much noise immunity as RS-485, but these devices
can provide signaling rates that exceed RS-485 capabilities. In addition to the increased
signaling rate, M-LVDS also provides multipoint operation with less power consumption than
RS-485.
Figure 2 shows the power advantage the SN65MLVD200 3.3V M-LVDS transceiver has over a
3.3V RS-485 transceiver, the MAX 3485E, for the setup in Figure 3. Both devices are 3.3-V
devices in the standard SN75176 footprint. Supply current measurements were taken at
different signaling rates with both the receiver and driver enabled in order to calculate power.
Figure 2 also shows that the M-LVDS device has a considerably higher maximum signaling rate
than the RS–485 part; 100Mbps
1
compared to 20Mbps.
While TIA/EIA-485 is better suited for longer distance applications, M-LVDS provides true multi-
point solutions with less power usage at greater speeds. The lower operating voltages of
M-LVDS are the reason for the lower power consumption but also the reason for the restriction
to shorter distances where noise coupling and differential attenuation through the interconnect
media are lower.
1
The 200Mbps M-LVDS devices, SN65MLVD201 and SN65MVLD203, can be found in the SN65MLVDS20x data sheet, SLLA463.





