下载
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Voltage References > APP 2008
Keywords: dc dc converters, voltage reference, converter, dc to dc
APPLICATION NOTE 2008
Accurate DC-DC Converter Minimizes Wasted
Power
Jun 02, 2003
Whether squeezing the last millijoule from your battery or operating a cooler CPU board, the goal is to
burn less power. For many loads the power dissipation varies as the square of the applied voltage, so
one approach is simply to minimize the supply voltage. Power dissipation equals V²/R in a resistive load
and CV²F in a CMOS load, where C is the internal CMOS capacitance and F is the frequency.
The consequence of this square law dependency is a 2% change in power dissipation for every 1%
change in voltage. Clearly, tight power control is a consequence of tight voltage control. To achieve that
goal, the circuit of Figure 1 produces an output voltage whose accuracy is far tighter than that of the
DC-DC converter's internal voltage, and without need for precision external resistors.
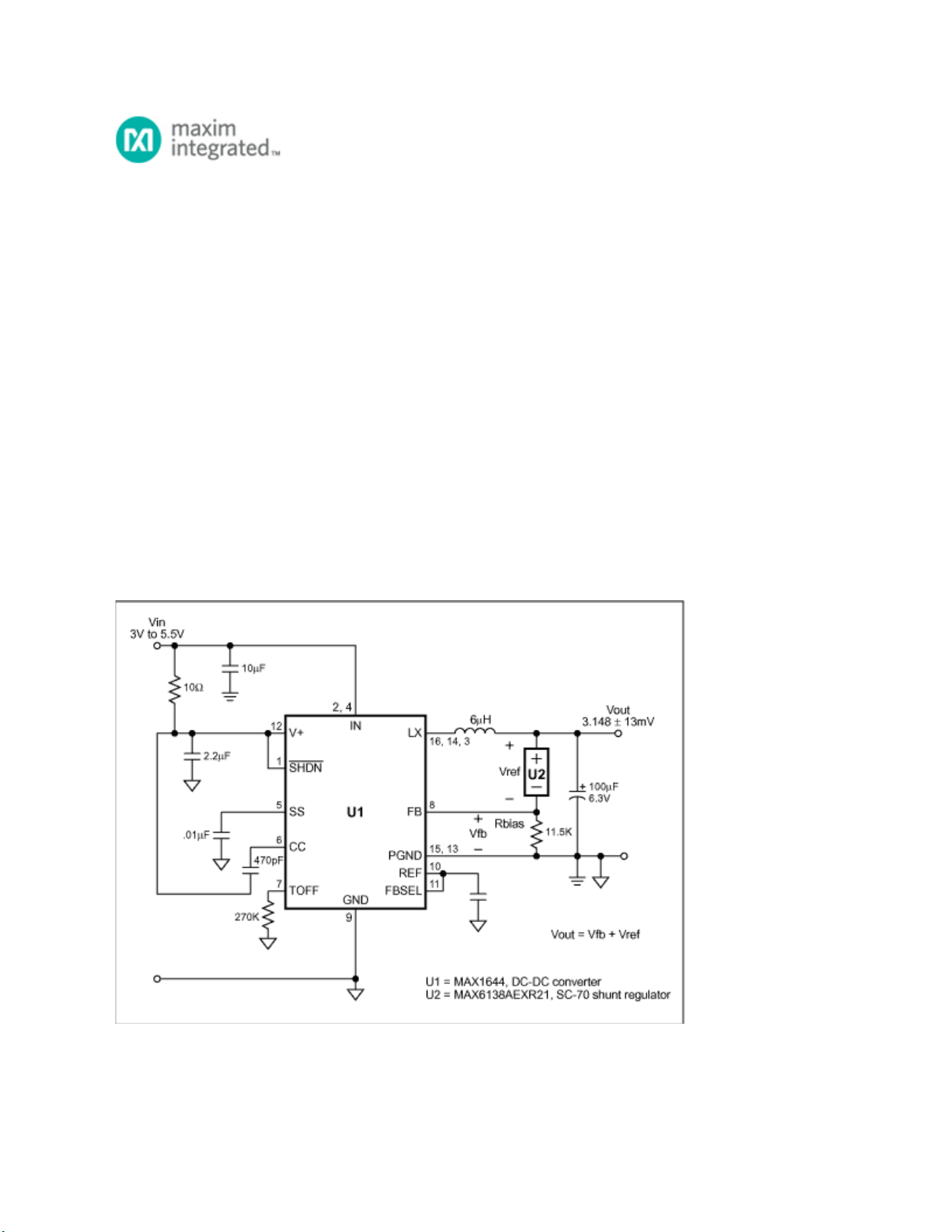
Figure 1. Substituting a shunt regulator (U2) for the customary resistive divider in this DC-DC converter
dramatically improves the output voltage accuracy.
Page 1 of 4