Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Optoelectronics > APP 2930
Keywords: SFP modules, MAX3740, MAX3735A, SFP laser drivers, ic safety features, supply voltage,
over-voltage protection, Zener diode, small form factor pluggable, SFP, laser drivers,
APPLICATION NOTE 2930
HFAN-02.4.0: Over-Voltage Protection for SFP
Laser Drivers [Application Brief]
Dec 15, 2003
Abstract: Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) Modules often require that various safety requirements be
met to prevent the optical output from exceeding pre-defined power limits. Using a Zener diode, over-
voltage protection can be integrated with the internal safety features of the MAX3740 and MAX3735A
SFP laser drivers.
Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) Modules often require that various safety requirements be met to
prevent the optical output from exceeding pre-defined power limits. The MAX3740 and MAX3735A SFP
laser drivers integrate many of these safety features on the IC. These devices are designed to be single-
point fault tolerant and also provide adjustable fault levels for the bias and monitor diode currents. These
features ensure safe and proper operation when the device is operated within its specified range.
In some SFP applications, it is required that the laser driver be disabled when the supply voltage has
exceeded (over-voltage) its normal operating range. Providing over-voltage protection can be easily
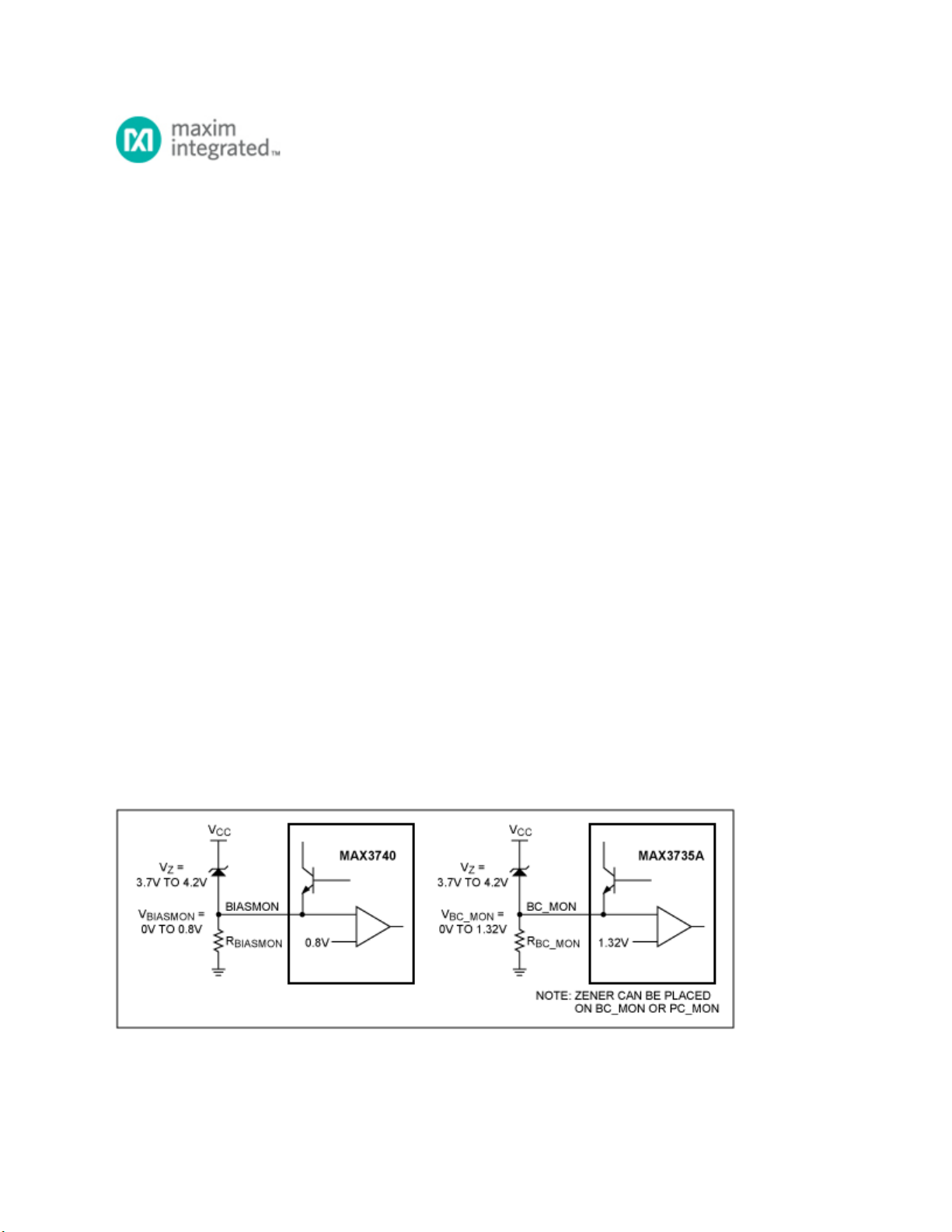
implemented when using the Maxim SFP laser drivers by placing a Zener diode as shown in Figure 1.
The potential of the BIASMON pin of the MAX3740 (Figure 1) is between 0V and 0.8V under normal
conditions. If the voltage at BIASMON exceeds approximately 0.8V, a fault is latched and the device
shuts down. When the voltage difference between V
CC
and BIASMON exceeds the reverse breakdown
voltage of the Zener diode, current will flow through the diode and into the resistor.
Figure 1. Zener diode placement.
The MAX3740 will then shutdown once the current has caused the voltage at BIASMON to exceed 0.8V.
Page 1 of 2