下载
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Microcontrollers > APP 3007
Keywords: logic-level translation, logic, data transfer rate
APPLICATION NOTE 3007
Logic-Level Translation
Jul 21, 2004
Abstract: Logic level translation techniques and pitfalls - and Maxim solutions.
Electronic design has changed considerably since the days when TTL and 5V CMOS were the dominant
standards for logic circuits. The increasing complexity of modern electronic systems has led to lower voltage
logic, which in turn can cause incompatibility between input and output levels for the logic families within a
system. It is not unusual, for example, that a digital section operating at 1.8V must communicate with an
analog subsection operating at 3.3V. This article examines the basics of logic operation and considers,
primarily for serial-data systems, the available methods for translating between different domains of logic
voltage.
The Need for Logic-Level Translation
The growth of digital ICs that feature incompatible voltage rails, lower V
DD
rails, or dual rails for V
CORE
and
V
I/O
has made the translation of logic levels necessary. The use of mixed-signal ICs with lower supply
voltages that have not kept pace with those of their digital counterparts also creates the need for logic-level
translation.
Translation methods vary according to the range of voltages encountered, the number of lines to be
translated (e.g., a 4-line Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) versus a 32-bit data bus), and the speed of the
digital signals. Many logic ICs can translate from high to low levels (such as 5V to 3.3V logic), but fewer can
translate from low to high (3.3V to 5V). Level translation can be accomplished with single discrete transistors
or even with a resistor-diode combination, but the parasitic capacitance inherent in these methods can
reduce the data-transfer rate.
Although byte-wide and word-wide level translators are available, they are not optimal for the < 20Mbps
serial buses discussed in this article (SPI, I²C, USB, etc.). Thus, translators that require large packages with
high pin counts and an I/O-direction pin are not meant for small serial and peripheral interfaces.
The Serial Peripheral Interface consists of the unidirectional control lines data in, data out, clock, and chip
select. Data in and data out are also known as master in, slave out (MISO) and master out, slave in (MOSI).
SPI can be clocked in excess of 20Mbps, and is driven by CMOS push-pull logic. As SPI is unidirectional,
translation in both directions on the same signal line is unnecessary. This makes level translation simpler,
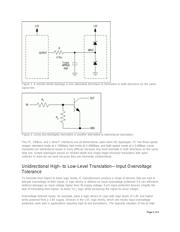
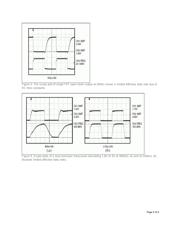
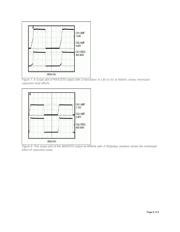
because you can employ simple techniques involving resistors and diodes (Figure 1) or discrete/digital
transistors (Figure 2).
Page 1 of 9