下载
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Power-Supply Circuits > APP 3753
Keywords: thermistor, buck converter, step-down converter, dc-dc converter, temperature compensation
APPLICATION NOTE 3753
Thermistor Linearizes Current Limit
Mar 17, 2006
Abstract: A resistive network that includes a thermistor is used to temperature-compensate the current-
limit input (ILIM) of a DC-DC converter.
Recent advances in the design of step-down DC-DC converters have eliminated the current-sense
resistor by substituting the drop across the low-side MOSFET (synchronous rectifier) instead. This
topology saves the cost and space of a sense resistor, and also provides a modest boost in efficiency.
One compromise imposed by the new approach, however, is a current-limit value dominated by the
MOSFET's on-resistance, which is highly temperature dependent.
Fortunately, the new DC-DC converters provide a pin that allows adjustment of the current-limit
threshold. By changing this threshold according to temperature, you can temperature-compensate the
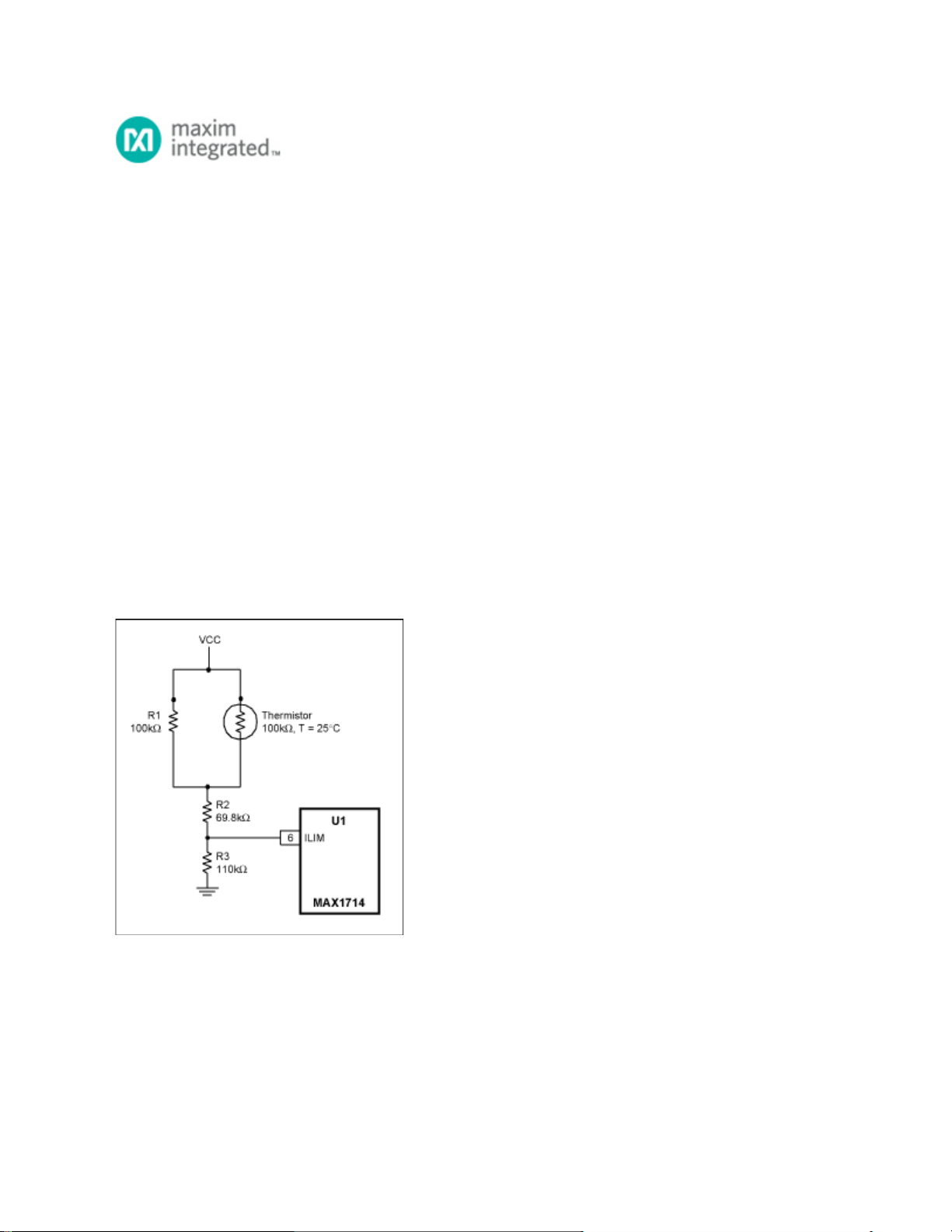
circuit's output-current limit. That task is readily accomplished with a thermistor as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. This resistive network temperature-compensates the current-limit input (ILIM) of a DC-DC
converter.
The linear input range for the ILIM input of U1 is 0.5V to 2.0V, which corresponds to current-limit
thresholds of 50mV to 200mV, respectively. For the default current-limit setting (100mV), the circuit has a
7.5A current limit at +25°C. As shown in Figure 2, however, the limit ranges from 9A at -40°C to 6A at
+85°C.
Page 1 of 3