下载

1 of 12
REV: 052203
OVERVIEW
This application note discusses how to use the recovered clock from a T1 or E1 span in a timing distribution
application. The BITS (building integrated timing supply) is one type of clock that is used extensively in
network synchronization. It is a master timing supply for all deployed equipment within a network requiring
synchronization. The term BITS is used in North America, but the rest of the world refers to this type of clock
as
a Synchronization
Supply Unit (SSU). The Dallas Semiconductor single-chip transceivers (SCTs) and line
interface units (LIUs) are excellent candidates for the front end of a BITS/SSU application or other timing
distribution models based on DS1 (T1) or E1 traffic.
SYNCHRONIZATION STANDARDS
ITU-T, ANSI, ETSI and Telcordia maintain requirements (Tables 1 and 2) for timing and network
synchronization. Within these documents, clocks are divided into different levels, or Stratums, that define the
accuracy and
stability for the timing. In the ANSI specifications, the most accurate clock level, Stratum 1, is
defined as a free-running clock with accuracy of better than 1x10
-11
. Cesium clocks are an example of a
Stratum 1 clock. Stratum 2 (Type II clocks in ITU-T specs) is the next level of clocks, followed by Stratum 3
(Type IV) and Stratum 4. Stratum 3E (Type III) was introduced as a level of timing between Stratum 2 and 3
and is typically used in SONET and SDH.
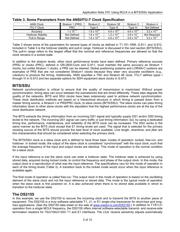
Table 1. North American Synchronization Standards
ELTIT CEPS
ANSI T1.101
Synchronization Interface Standards
GR-378-CORE
Generic Requirements for Timing Signal Generators
GR-436-CORE
Digital Network Synchronization
GR-253-CORE
Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) Transport Systems: Common Generic Criteria
GR-1244-CORE
Clocks for the Synchronized Network: Common Generic Criteria
GR-2830-CORE
Primary Reference Sources: Common Generic Criteria
Table 2. ITU Synchronization Standards
ELTIT CEPS
G.703
Physical/Electrical Characteristics of Hierarchical Digital Interfaces
G.704
Synchronous Frame Structures Used at 1544, 6312, 2048, 8488, and 44736kbps Hierarchical
Levels
G.810
Definitions and Terminology For Synchronized Networks
G.811
Timing Characteristics of Primary Reference Sources
G.812
Timing Requirements for Slave Clocks for use as Node Clocks in Synchronized Networks
G.813
Timing Characteristics of SDH Equipment Slave Clocks
G.824
Control of Jitter and Wander Within Digital Networks That are Based on the 1544kbps
Hierarchy
A
pplication Note 370
Using RCLK in a BITS/SSU Application
www.maximintegrated.com