下载

®
©
1999 Burr-Brown Corporation AB-167 Printed in U.S.A. October, 1999
COMPARING THE ADS1201 TO THE CS5321
By Robert Schreiber
INTRODUCTION
The ADS1201 is a high dynamic range, low-cost, ∆Σ modu-
lator. Although the performance of the ADS1201 can be
assessed with the DEM-ADS1201U demonstration board,
there have been numerous independent evaluations of the
ADS1201 in a variety of systems. The comparisons were
undertaken due to the high performance and significant cost
savings of the ADS1201 over alternative solutions. By direct
comparison to other solutions, the exceptional value of the
ADS1201 becomes apparent.
The intent of this application bulletin is to provide a simple
means of comparing the operation of the ADS1201 ∆Σ
modulator to Crystal’s CS5321 ∆Σ modulator. It is not the
intent of this document to describe the theory or the opera-
tion behind ∆Σ modulators, it is merely to provide the
methodology, configuration, and results of tests that were
performed using these modulators with a common digital
filter. The theory of operation and device specifications can
be found in the individual data sheets for these parts.
TEST OVERVIEW
The tests were performed by an independent evaluator,
Martin Company, using the CS5321 evaluation board. The
CS5321 evaluation board was designed to demonstrate the
performance of the CS5321 ∆Σ modulator with the CS5322
digital filter. The CS5321 accepts an analog input and
outputs a high-rate, low-resolution bit-stream to the CS5322
digital filter. The result from the digital filter is a low-rate,
high resolution (24-bit) digital representation of the analog
value. Since the basic operation of the ADS1201 and CS5321
is the same, the ADS1201 modulator can be used with the
CS5322 filter to obtain the same 24-bit digital representa-
tion. The following paragraph is an overview of how the
CS5321 evaluation board was setup to accommodate both
the ADS1201 and the CS5321.
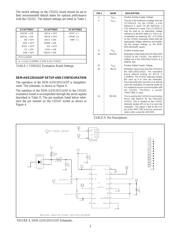
The CS5321 was removed from the evaluation board and
replaced with socketed pins. The ADS1201 was evaluated
by inserting the DEM-ADS1201UADP board into the sock-
eted pins. It should be noted that the CS5321 evaluation
board was optimized to demonstrate the performance of the
CS5321. The CS5321 evaluation board does not demon-
strate the optimum performance of the ADS1201, therefore,
the actual in-circuit performance of the ADS1201 with the
digital filter may be significantly better than the test results
indicate.
Some key points about the comparison are listed below:
1. HBR = 1 mode was used with a MCLK frequency of
1.024MHz, which according to the CS5321 specification,
gives the best performance of the part. In this mode, the
CS5321 internally divides MCLK by 4, resulting in an
MDATA rate of 256kHz (to the CS5322 digital filter).
The ADS1201 does not internally divide MCLK by 4; the
ADS1201 shifts data out at the MCLK rate. Therefore an
external counter (divided by 4) was required to slow the
MCLK to the ADS1201 and thus, the MDATA rate from
the ADS1201 to the CS5322. Due to this limitation of the
CS5322 digital filter, the ADS1201 MCLK rate was run
at 256kHz, not the optimal rate of 320kHz.
2. The ADS1201 operates from a single +5VDC supply and
has a differential voltage range of ±5V with respect to the
A
IN+
and A
IN–
pins (the differential voltage range is ±10V
when V
BIAS
is used).
The CS5321 operates from both a +5VDC and –5VDC
supply and has a single-ended voltage range of ±4.5V
with respect to ground.
3. The CS5321 uses an LTC1019-4.5 voltage reference. The
ADS1201 requires a 2.5V reference. The DEM-
ADS1201UADP demo board allows two options for the
ADS1201 reference. First, the REF1004-2.5 on the DEM-
ADS1201UADP board can be used. Alternately, an
LTC1019-2.5 can be inserted in the socket on the CS5321
demo board in place of the LTC1019-4.5. The REF1004-
2.5 offers comparable performance to the LTC1019 at a
lower cost.
SBAA039